Experiencing sudden hearing loss or the intrusive ringing of tinnitus can feel overwhelming and confusing. These conditions often leave people searching for answers, wondering what’s happening and why. This post explains the potential causes of sudden hearing loss and tinnitus, the connection between them, and why seeking medical attention quickly is so important. By understanding these conditions, you’ll be better prepared to take the right steps toward managing or improving your hearing health.
Sudden Hearing Loss
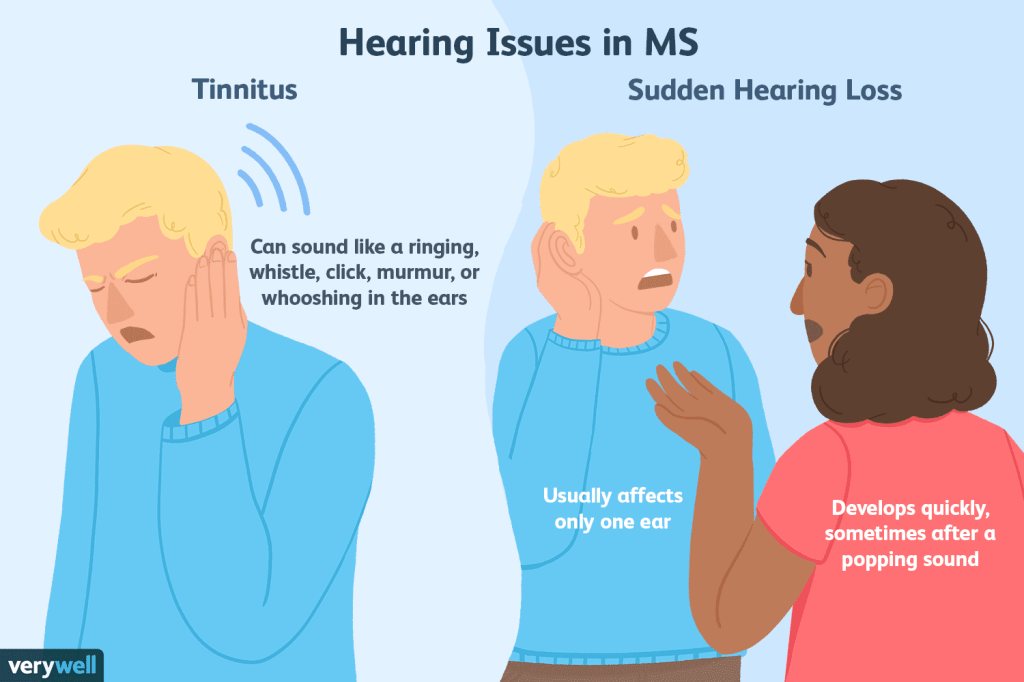
Sudden hearing loss, often referred to as sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL), is a rapid loss of hearing, typically occurring in one ear. It can happen over a span of a few hours or days, and in some cases, it might be accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the affected ear. The underlying cause of SSHL is not always identifiable, but it is believed to be connected to viral infections, autoimmune diseases, or circulatory problems that affect the inner ear.
The symptoms of SSHL can be distressing, as they often include a sudden inability to hear clearly or a complete loss of hearing in one ear. Some individuals may also experience dizziness or vertigo. Due to its sudden onset, SSHL is considered a medical emergency, and it is crucial to seek immediate attention from a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the chances of recovery.
Treatment for SSHL typically involves corticosteroids, which help reduce inflammation and swelling in the cochlea. In some cases, antiviral medications or therapies aimed at improving blood flow to the inner ear may be considered. Prompt intervention is key, as the effectiveness of treatment often diminishes if delayed beyond a critical period following the onset of symptoms.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is characterized by the perception of sound in the absence of an external source. It is often described as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or humming in the ears. Tinnitus can vary in intensity and may be constant or intermittent. Unlike sudden hearing loss, tinnitus is not typically considered a medical emergency, but it can still be incredibly disruptive to daily life.
The causes of tinnitus are diverse, ranging from exposure to loud noises, ear infections, and age-related hearing loss to more complex conditions like Meniere’s disease or temporomandibular joint disorders. Stress, anxiety, and certain medications can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of tinnitus.
Managing tinnitus often involves addressing the underlying cause, if identifiable, and implementing strategies to reduce its impact. Sound therapy, which uses external sounds to mask or alter the perception of tinnitus, is a common approach. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be beneficial, helping individuals develop coping strategies to manage the emotional and psychological effects of tinnitus. In some cases, hearing aids may be recommended, particularly if tinnitus is accompanied by hearing loss.
Conclusion
Sudden hearing loss and tinnitus are conditions that require careful attention and management. While SSHL demands immediate medical intervention to maximize recovery potential, tinnitus management often involves a more individualized approach tailored to the specific needs of the patient. By understanding these conditions and exploring available treatments, individuals affected by sudden hearing loss or tinnitus can take proactive steps toward improving their auditory health and overall well-being. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of sudden hearing loss or persistent tinnitus, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.






Leave a comment