Many people know about TMJ (temporomandibular joint disorders) and tinnitus, but how often do we consider their connection? Surprisingly, these two conditions frequently go hand in hand, affecting millions. If you or someone you know grapples with jaw pain or ringing in the ears, you’re not alone. Let’s take a closer look at what TMJ and tinnitus are, how they intertwine, and what you can do about it.
What is TMJ?
TMJ disorders affect how your jaw functions and can manifest in various uncomfortable ways. This joint connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing you to eat, speak, and express yourself. When something goes wrong, it can lead to pain and dysfunction.
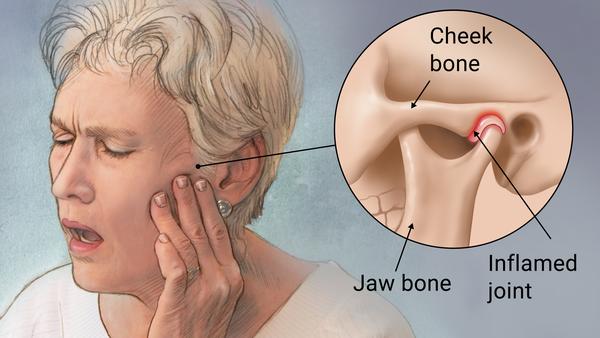
Symptoms of TMJ Disorders
It’s essential to recognize the signs of TMJ disorders. Common symptoms include:
- Jaw pain: This can radiate to your face, neck, and even ears.
- Headaches: Often mistaken for migraines, these can be frequent and debilitating.
- Difficulty chewing: You may find it hard to open or close your mouth fully.
- Clicking sounds: Many experience a popping or clicking noise when moving their jaw.
- Ear discomfort: Some report a sensation of fullness or pain in their ears.
Causes of TMJ Disorders
What leads to these issues? Several factors can contribute to TMJ disorders:
- Jaw injury: An accident or trauma can directly impact the jaw joint.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism): Stress or misaligned teeth can lead to grinding, putting pressure on the joint.
- Stress: Increased tension can cause clenching, exacerbating TMJ issues.
- Arthritis: Conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joint.
Understanding these causes helps you realize that relief may be possible with the right approach.
Understanding Tinnitus
Tinnitus is another condition that affects many people, but often without clear answers. It’s characterized by hearing ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds when there’s no external source.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
Many factors might lead to tinnitus, including:
- Exposure to loud noise: Frequent loud sounds can damage the inner ear.
- Ear infections: Infections can cause inflammation and fluid buildup, leading to symptoms.
- Age-related hearing loss: As we age, the auditory system naturally deteriorates.
- Earwax buildup: Excess wax can block sound, resulting in tinnitus symptoms.

How Tinnitus is Diagnosed
Diagnosing tinnitus often involves a detailed process:
- Hearing evaluations: An audiologist may conduct tests to gauge your hearing ability.
- Patient history: Your doctor will likely ask about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle.
Gaining a clear diagnosis can empower you to pursue effective treatment options.
The Link Between TMJ and Tinnitus
Research is uncovering how TMJ disorders and tinnitus relate. Many patients report experiencing both issues, leading experts to explore their connection.
Shared Symptoms and Overlapping Mechanisms
Both TMJ and tinnitus share some symptoms, such as:
- Ear pain: The discomfort from TMJ can feel like an ear issue.
- Muscle involvement: Both conditions often engage similar muscle groups in the jaw and neck.
Understanding this overlap may help healthcare providers pinpoint effective treatments for both issues.
Clinical Evidence and Studies
Some studies indicate that individuals with TMJ disorders are more prone to experience tinnitus. For instance, one research review found a significant correlation between these conditions. However, more exploration is needed to understand the direct relationship fully.
Treatment Options for TMJ and Tinnitus
Managing both TMJ and tinnitus often requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on symptom relief and addressing underlying causes.
Physical Therapy and Jaw Exercises
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in managing TMJ disorders and may help alleviate tinnitus symptoms as well. Techniques include:
- Stretching exercises: Gentle stretches can improve jaw movement and reduce tightness.
- Posture improvement: Good posture can alleviate strain on your jaw and neck muscles.
- Massage: Targeted massage can release tension in the jaw area.
These strategies may not only ease jaw discomfort but also reduce the perception of ringing in the ears.
Medications and Other Interventions
Various medications and alternative therapies can assist in managing symptoms:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help.
- Muscle relaxants: These may be prescribed to relieve muscle tension linked to TMJ.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): This method can help manage the stress and anxiety often tied to these conditions.
- Hearing aids: For those with tinnitus caused by hearing loss, hearing aids can assist in noise management.
Consider discussing a comprehensive treatment plan with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Living with TMJ and tinnitus can be challenging, but it’s crucial to recognize that relief is attainable. By understanding these conditions and their connection, you empower yourself to seek appropriate care. If you’re dealing with jaw pain or persistent ringing in your ears, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Remember, you don’t have to navigate this journey alone. Help is available, and taking the first step can lead to a brighter, more comfortable future.






Leave a comment