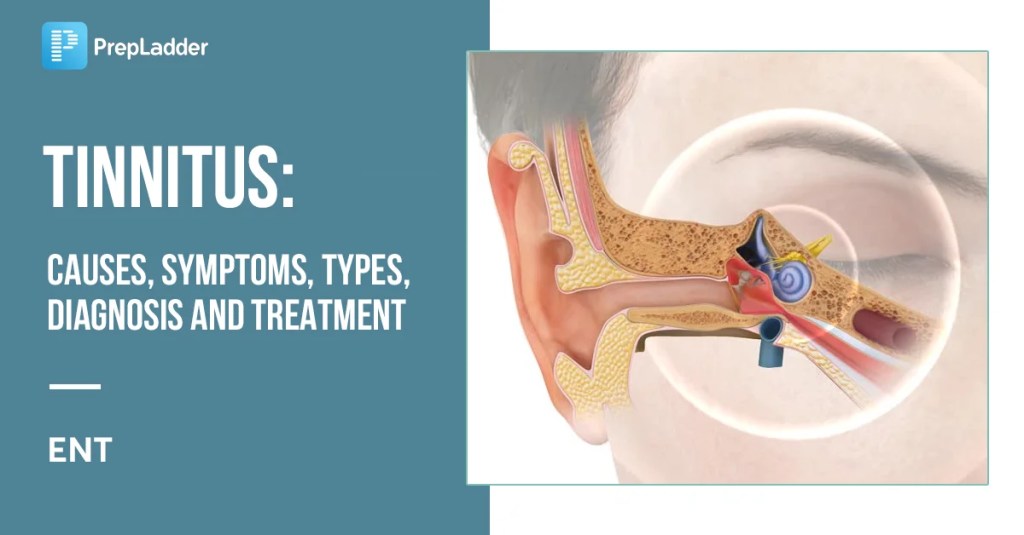
Tinnitus and anxiety often feel like a relentless loop—one feeds the other, creating a cycle that’s hard to escape. But there’s hope. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a practical solution to help break this connection. By addressing the way our minds respond to sound and stress, CBT provides tools for managing both conditions more effectively. In this post, we’ll explore how CBT works and why it’s a promising option for those looking to reclaim control.

Understanding the Tinnitus-Anxiety Connection
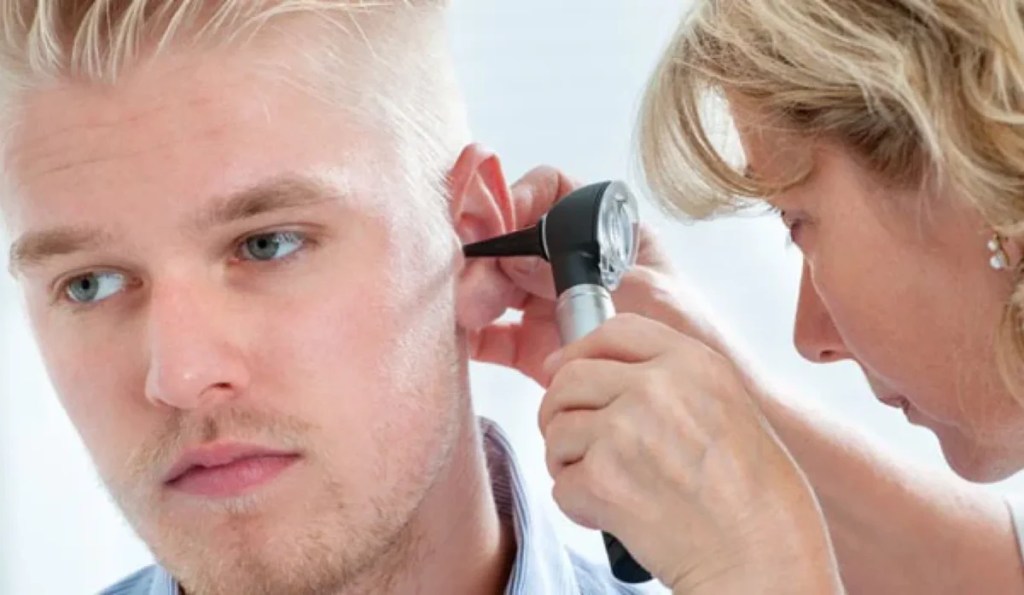
Tinnitus affects millions of people worldwide, and while it is generally not a sign of a serious underlying condition, the constant presence of phantom sounds can lead to distress and anxiety. The relationship between tinnitus and anxiety is complex. Anxiety can increase the brain’s sensitivity to tinnitus, making it appear louder and more intrusive. Conversely, the persistent nature of tinnitus can lead to heightened anxiety, as individuals become increasingly focused on and stressed by the condition.
The Role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
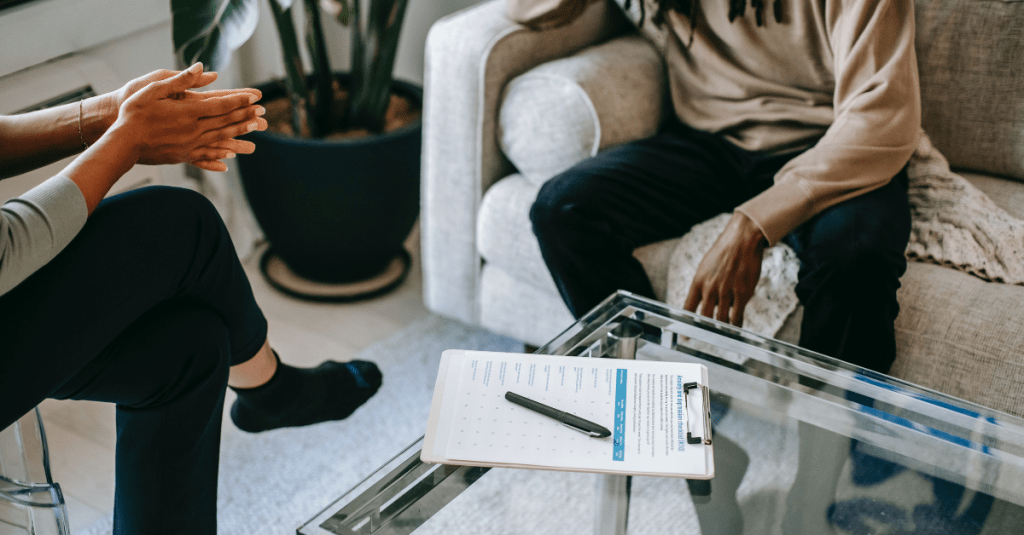
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, a form of psychological treatment, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in treating anxiety related disorders. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, supporting individuals in developing healthier responses to stressors.
When applied to tinnitus, CBT offers several benefits:
1. Reduction of Negative Thought Patterns: CBT helps individuals recognize and challenge maladaptive beliefs about tinnitus, such as the idea that it will worsen over time or that it is a sign of a severe health issue. By reframing these thoughts, individuals can reduce the anxiety associated with tinnitus.
2. Stress Management Techniques: CBT equips individuals with tools to manage stress effectively. Techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and controlled breathing can lower overall anxiety levels, reducing the perceived intensity of tinnitus.
3. Improved Emotional Regulation: CBT encourages individuals to develop better emotional regulation skills, allowing them to respond calmly to tinnitus rather than reacting with panic or distress. This shift in response can diminish the cycle of anxiety and tinnitus.
4. Enhanced Coping Strategies: Through CBT, individuals can learn coping strategies tailored to their specific experiences with tinnitus. This personalized approach empowers them to handle tinnitus-related challenges confidently.
Breaking the Cycle
The cycle of tinnitus and anxiety can be debilitating, but CBT offers a pathway to breaking free from its grip. By addressing both the psychological and emotional aspects of tinnitus, CBT provides a holistic approach that enhances overall well-being.
For those struggling with tinnitus and anxiety, seeking professional help from a therapist trained in CBT can be a transformative step. While CBT may not eliminate tinnitus entirely, it can significantly improve quality of life, helping individuals regain control and reduce the impact of tinnitus on their daily lives.
In conclusion, the interplay between tinnitus and anxiety underscores the importance of addressing both conditions simultaneously. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy stands out as a powerful tool in breaking the cycle, offering hope and relief to those affected. Through CBT, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms effectively, paving the way for a more peaceful and fulfilling life despite the presence of tinnitus.